The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is a non-regulatory agency of the United States Department of Commerce that promotes innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST has been instrumental in shaping cybersecurity guidelines for organizations to mitigate cyber threats and protect sensitive information.
Toc
Introduction to NIST Incident Response Framework
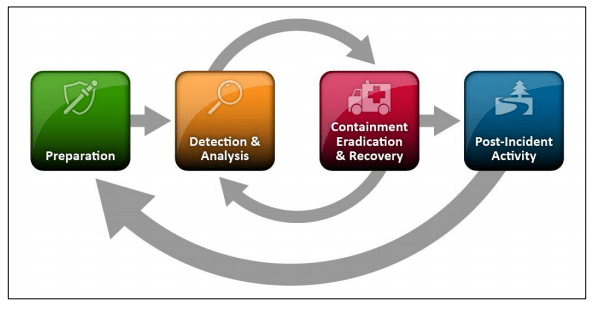
The NIST Incident Response Framework provides a structured approach for organizations to effectively respond to cyber incidents. It is based on the five key steps of preparation, detection and analysis, containment, eradication and recovery, and post-incident activities.
What is NIST and its role in Cybersecurity?
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has long been at the forefront of promoting robust cybersecurity practices. Founded in 1901, NIST is a part of the U.S. Department of Commerce and is dedicated to advancing measurement science, standards, and technology. In the realm of cybersecurity, NIST provides comprehensive guidelines and frameworks designed to help organizations of all sizes protect their information systems and data.
Brief Overview of the NIST Incident Response Framework
NIST’s Incident Response Framework is a structured methodology designed to guide organizations through the process of effectively managing and mitigating cybersecurity incidents. It encompasses a series of best practices and procedures that ensure a systematic approach to incident response, from initial preparation to post-incident analysis.
Why is Cybersecurity Important?
With the increasing number of cyber attacks targeting organizations, it has become crucial for companies to prioritize cybersecurity. A single security breach can have catastrophic consequences such as financial loss, damage to reputation, and disruption of operations. Therefore, implementing effective cybersecurity measures is essential to safeguard data and prevent potential damages.
Benefits of nist incident response
NIST’s guidelines for incident response provide a comprehensive approach to managing and responding to cyber threats. By following these guidelines, organizations can benefit in several ways:
- Improved Incident Detection and Response: NIST’s guidelines help organizations establish procedures for detecting potential security incidents and reacting promptly to mitigate their impact.
- Optimized Resources and Time: With a clearly defined incident response plan in place, organizations can save valuable time and resources by responding efficiently to security incidents.
- Reduced Financial Loss: Effective incident response measures can prevent or minimize financial losses that may result from cyber attacks.
- Enhanced Organizational Resilience: By implementing incident response procedures, organizations can improve their resilience to cyber threats and recover quickly from any potential damages.
Key Insights from NIST’s Guidelines
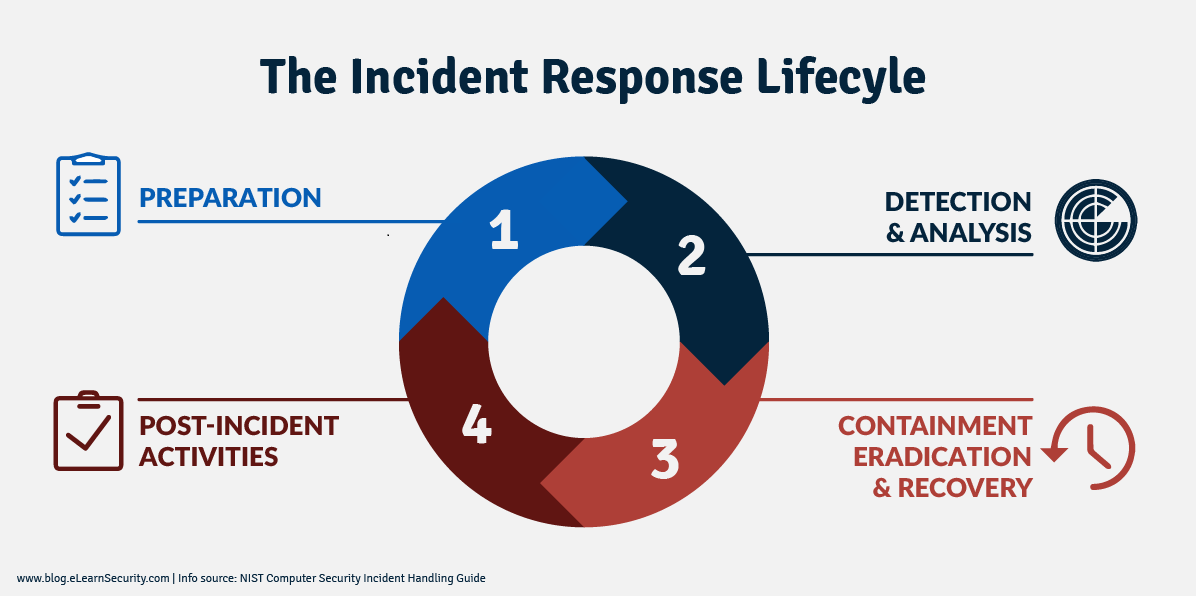
NIST’s guidelines for incident response are based on four key phases: preparation, detection and analysis, containment, eradication and recovery. Let’s take a closer look at each of these phases:
1. Preparation
The preparation phase involves developing an incident response plan that outlines the steps to be taken in case of a security breach. This plan should include roles and responsibilities of team members, communication protocols, and procedures for documenting and reporting incidents.
Policies and Procedures: During the preparation phase, it is also essential to establish and document policies and procedures that will guide the incident response process. These policies should cover aspects such as defining what constitutes a security incident, setting criteria for escalating incidents, and detailing the steps for incident investigation and response. Doing so ensures that the response team operates with a clear understanding of the protocols, reducing confusion and ensuring a swift response.
2. Detection and Analysis
The detection and analysis phase focuses on identifying and understanding the security incident. This involves continuous monitoring of systems and networks to spot any suspicious activity or potential threats. Tools such as intrusion detection systems (IDS), security information and event management (SIEM) systems, and log analysis tools are vital in this phase to detect anomalies and gather relevant data.
Incident Classification: Once a potential incident is detected, it is important to classify its severity and scope. Proper classification helps in prioritizing the response and allocating resources efficiently. Incidents can be categorized based on various factors such as the type of attack, the level of impact, and the affected systems and data.
Root Cause Analysis: Understanding the root cause of the incident is crucial for effective mitigation. Root cause analysis involves examining the gathered data to determine how the breach occurred, what vulnerabilities were exploited, and what systems were impacted. This information is vital for formulating a targeted response strategy and for preventing similar incidents in the future.
1. https://alightmotion.top/unlocking-efficiency-growth-with-legal-ai-tools-a-guide-for-attorneys/
4. https://alightmotion.top/elevate-your-expertise-the-power-of-a-computer-science-masters-degree/
5. https://alightmotion.top/data-rooms-the-key-to-enhanced-business-protection-and-efficiency/
3. Containment, Eradication, and Recovery
Following detection and analysis, the next step is to contain the threat to prevent further damage. This can involve isolating affected systems, blocking malicious traffic, or applying temporary fixes. The goal is to limit the spread of the incident and protect unaffected resources.
After containment, the eradication phase aims to eliminate the cause of the incident. This can include removing malware, patching vulnerabilities, or addressing misconfigurations. Thorough validation is necessary to ensure that the threat has been completely removed.
Finally, the recovery phase focuses on restoring systems and services to normal operation. This may involve restoring from backups, rebuilding systems, and ensuring that affected services are operating securely. Recovery efforts should also include monitoring to detect any signs of persistent threats.
4. Post-Incident Activity
Post-incident activity is crucial for learning and improving future incident response. This phase includes conducting a thorough review of the incident and the response actions taken. It’s important to document lessons learned, areas for improvement, and any changes needed in the incident response plan.
Reporting and Documentation: Comprehensive documentation and reporting of the incident are essential. This should include a detailed timeline of events, the actions taken during detection, analysis, and mitigation, as well as any communication with stakeholders. Proper documentation ensures accountability and provides a valuable resource for training and future reference.
Continuous Improvement: The insights gained from post-incident analysis should be used to update and refine the incident response plan, policies, and procedures. Continuous improvement ensures that organizations remain agile and prepared to face evolving cyber threats.
By adhering to NIST’s guidelines, organizations can build a robust incident response capability that not only mitigates the impact of cyber incidents but also strengthens overall cybersecurity posture.
Application of NIST Framework in Enhancing Incident Response Capabilities
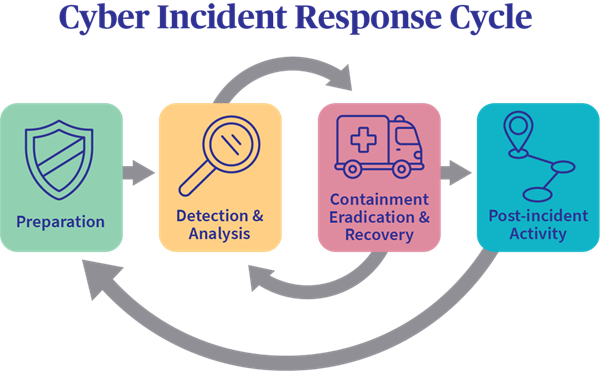
The NIST framework provides a structured approach for organizations to develop and improve their incident response capabilities.
Key benefits of applying this framework
Here are some key benefits of applying this framework:
- Standardization of Processes: Implementing the NIST framework allows organizations to standardize their incident response processes, ensuring that all team members follow a consistent approach. This reduces the likelihood of oversight or miscommunication during critical incidents.
- Improved Coordination: A clearly defined framework enhances coordination among different teams and departments. By aligning their response efforts, organizations can expedite decision-making and response actions, thereby limiting the impact of security incidents.
- Enhanced Training and Preparedness: The NIST framework emphasizes the importance of regular training and preparedness exercises. By conducting simulated incident scenarios, organizations can test their response plans, identify gaps, and ensure that team members are well-versed in their roles and responsibilities during an actual incident.
- Efficient Resource Management: Structured incident response processes enable more efficient allocation and utilization of resources. With predefined roles and responsibilities, organizations can quickly mobilize the necessary personnel and technical resources required to handle incidents effectively.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to NIST guidelines can also help organizations meet regulatory requirements and industry standards for cybersecurity. This not only minimizes the risk of non-compliance penalties but also enhances the organization’s reputation and trust among stakeholders.
By integrating the NIST framework into their incident response strategies, organizations can significantly enhance their ability to detect, respond to, and recover from cyber incidents, thereby fortifying their overall security posture. Moreover, the continual improvement aspect of the framework ensures that organizations remain adaptable in the face of evolving cyber threats.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Equifax Data Breach A Case of Insufficient Response: The Equifax data breach of 2017, which exposed the personal information of over 147 million people, highlighted the critical importance of an effective incident response strategy. The breach was partly attributed to Equifax’s failure to follow established cybersecurity practices, including timely patching of vulnerabilities and effective monitoring of system activity. Implementing the NIST framework could have potentially mitigated the impact of the breach.
Sony PlayStation Network Hack Implementation of NIST Framework: In 2011, Sony’s PlayStation Network suffered a massive data breach that compromised the personal information of 77 million users. Following the breach, Sony adopted the NIST framework to overhaul its incident response strategy. The implementation of NIST guidelines allowed Sony to significantly improve its incident detection and response capabilities, reducing the likelihood of future breaches.
Maersk NotPetya Attack Lessons Learned from NIST: The NotPetya ransomware attack of 2017 crippled the global shipping giant Maersk, causing an estimated $300 million in damages. In the aftermath, Maersk implemented the NIST framework to enhance its cybersecurity defenses. By adopting NIST’s incident response principles, Maersk was able to rebuild its IT infrastructure and strengthen its resilience against future cyber threats.
Best Practices for Integrating NIST Incident Response
1. https://alightmotion.top/elevate-your-expertise-the-power-of-a-computer-science-masters-degree/
2. https://alightmotion.top/unlocking-efficiency-growth-with-legal-ai-tools-a-guide-for-attorneys/
3. https://alightmotion.top/the-ultimate-guide-to-ai-recruiting-tools-streamline-hiring-in-2024/
Implementing the NIST framework effectively requires a combination of strategic planning, regular training, and proactive measures. Below are some best practices to consider:
1. Develop a Comprehensive Incident Response Plan
A detailed incident response plan is the cornerstone of any effective cybersecurity strategy. The NIST framework provides guidelines for developing and maintaining this plan. Ensure that the plan includes clear procedures for detection, analysis, containment, eradication, and recovery. This structured approach will help the organization respond swiftly and efficiently to incidents.
2. Conduct Regular Training and Drills
Regular training sessions and simulation exercises are essential for preparing your incident response team. These practices help team members familiarize themselves with their roles and responsibilities and keep their skills sharp. By conducting drills that mimic real-world scenarios, organizations can identify weaknesses in their response plan and address them proactively.
3. Implement Continuous Monitoring
Continuous monitoring of networks and systems is critical for early detection of potential threats. Utilize advanced monitoring tools and technologies to identify unusual activities or vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. Establish a baseline of normal activity to help distinguish between legitimate and potentially harmful actions.
4. Collaborate and Share Information
Effective incident response often involves collaboration with external entities such as industry partners, government agencies, and cybersecurity organizations. Sharing information about threats, vulnerabilities, and effective mitigation strategies can help the broader community strengthen their defenses. Participate in Information Sharing and Analysis Centers (ISACs) and other collaborative platforms to stay informed about emerging threats and best practices.
5. Update and Test Your Plan Regularly
Cyber threats are constantly evolving, so your incident response plan should be updated regularly to reflect the latest threat intelligence and technological advancements. Periodically review and test the plan to ensure its effectiveness. Incorporate feedback from post-incident reviews and adjust your strategies to address any identified gaps or weaknesses.
6. Leverage Advanced Technologies
Incorporating advanced technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) can enhance your incident response capabilities. These technologies can help identify patterns indicative of cyber threats, automate response actions, and analyze large volumes of data more efficiently than traditional methods.
7. Ensure Executive Support
Gaining support from executive leadership is crucial for the success of an incident response strategy. Ensure that top management understands the importance of cybersecurity and is willing to allocate the necessary resources for effective incident response. Executive buy-in also helps in enforcing policies and fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness throughout the organization.
Conclusion
In conclusion, integrating the NIST Incident Response framework into your cybersecurity strategy is not just about adhering to best practices; it’s about building a robust, agile, and responsive defense system against the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats. The framework’s structured approach to incident detection, response, and recovery provides a comprehensive roadmap that can significantly reduce the impact and severity of cyber incidents.
Furthermore, by committing to continuous improvement and regular updates, organizations can ensure that their incident response plans remain aligned with the latest security trends and threat landscapes. This proactive stance not only helps in mitigating current threats but also equips organizations to better handle future challenges, thereby safeguarding critical assets and maintaining stakeholder trust.
Ultimately, the success of an incident response strategy hinges on the collective efforts of the entire organization, from executive leadership to frontline employees. By fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness and collaboration, and by leveraging advanced technologies, organizations can create a resilient security posture that stands the test of time. Through diligent planning, regular training, and an unwavering commitment to cybersecurity excellence, the adoption of the NIST framework can transform how organizations defend against, respond to, and recover from cyber threats.